CSS Selectors in Selenium WebDriverCSS Selectors (Cascading Style Sheets) are a powerful way to locate elements on a web page for Selenium automation. They are fast, flexible, and enable precise targeting of web elements.
Types of CSS Selectors
1. ID Selector (#)
The # symbol is used to select an element by its unique id attribute.
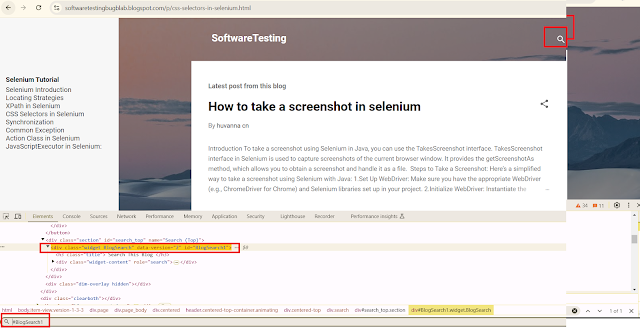
HTML:<div class="widget BlogSearch" data-version="2" id="BlogSearch1">
Ways to Write CSS for IDs:
Using Tag Name and ID :
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("div#BlogSearch1"));
Directly by ID:
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("#button"));
Using Tag Name with Attribute :
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("input[id='button']"));
2. Class Selector (.)
The . symbol is used to select elements by their class name.
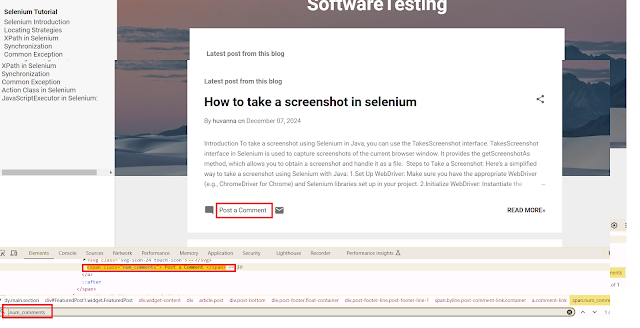
HTML:<span class="num_comments">Post a Comment</span>
Ways to Write CSS for Classes:
Using Tag Name and Class Name:
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("div.num_comments"));
Directly by Class Name:
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector(".num_comments"));
Using Tag Name with Attribute:
HTML:
<div class="widget Attribution" data-version="2" id="Attribution1">
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("div[id='Attribution1']"));
3. Attribute Selector
Selects elements based on their attributes. Useful when no IDs or classes are available.
HTML:
<div id="click" class="menu" style="display"></div>
Syntax:
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("div[style='display']"));
Other attributes like name, placeholder, title, and type can also be used.
4. ID and Attribute Selector
Combines an ID selector with an attribute selector for more specific targeting.
Syntax:
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("<tagname>#<id>[<attribute>='<value>']"));
HTML:
<input id="Add" class="button" type="submit">Submit</input>
Example Code:
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("input#Add[type='submit']"));
5. Class and Attribute Selector
Combines a class selector with an attribute selector.
Syntax:
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector(".<class-name>[<attribute>='<value>']"));
HTML:
<input class="form-control" placeholder="Enter your message" />
Example:
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector(".form-control[placeholder='Enter your message']"));
6. Substring Matching
Substring selectors allow partial matches on attribute values.
Common Substring Selectors:
Starts With (^=): Selects elements where the attribute value starts with a specific text.
HTML:
<input type="text" name="username" />
<input type="text" name="useremail" />
Example Code:
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("input[name^='user']"));
Ends With ($=): Selects elements where the attribute value ends with a specific text.
HTML:
<input type="text" name="emailUser" />
Example Code:
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("input[name$='User']"));
Contains (*=): Selects elements where the attribute value contains specific text.
HTML:
<input type="text" name="userControlPanel" />
Example Code:
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("input[name*='Control']"));
ConclusionCSS Selectors provide a versatile way to locate elements in Selenium, offering precision and flexibility. Mastering these techniques can greatly enhance your automation scripts, especially in complex DOM structures.



Comments
Post a Comment